Introduction to Industrial IoT
Have you ever been enamoured by how immaculately adventures are taking on development? You’ve caught wind of or learned about the Modern Web of Things (IIoT). Notwithstanding, what’s the importance here, and why might it be fitting as far as we’re concerned to mind? Modern IoT (IIoT) is using IoT advances in industrial settings. It includes interfacing apparatus, gear, and sensors to gather and examine information for streamlining fabricating processes, proactive support, and working on general effectiveness and efficiency in areas like assembling energy and operations.
The Rise of Industrial IoT
-
What is Industrial IoT?
It’s a little brainy cousin of the Internet of Things (IoT). While IoT generally refers to connected devices we use daily, IIoT specifically targets industrial applications. Think of factory machines communicating with each other, optimizing operations without human intervention.
-
Critical differences between IoT and IIoT
While your home assistant or wearable fitness tracker operates under IoT, industrial applications have unique requirements. The primary differences lie in applications’ scale, security, and complexity.
Benefits of IIoT
-
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
Imagine a factory where machines preemptively schedule their maintenance. It’s not science fiction but a reality, thanks to IIoT. Devices communicate and analyze performance data in real-time, reducing breakdowns and improving overall efficiency.
-
Cost Savings
Fewer breakdowns mean less fixed costs. Furthermore, proficient activities diminish wastage, meaning huge business cost investment funds. Modern IoT (IIoT) cost reserve funds result from working on functional productivity, decreasing margin time through prescient upkeep, enhancing asset assignment, and smoothing out the inventory network. Organizations can settle on informed choices, diminish squandering, and, finally, slice work costs thanks to the information-driven bits of knowledge the IIoT gives, which works on their intensity and productivity.
-
Enhanced Safety Measures
Safety is paramount in industries. With IIoT, machines can detect potential hazards, shutting down automatically or alerting human operators.
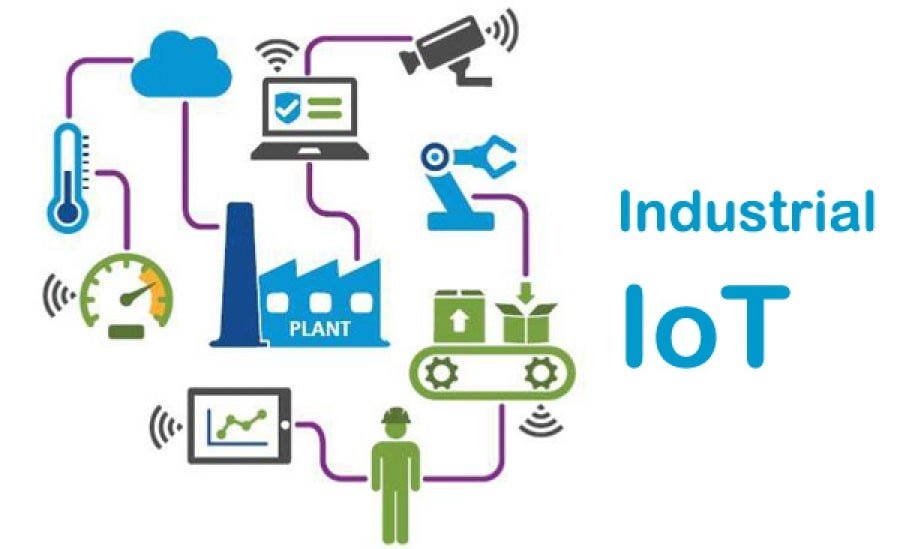
Real-World Applications of IIoT
-
Manufacturing
Savvy processing plants are, as of now, not simply an idea. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) optimizes manufacturing processes, reducing downtime and raising product quality. IoT applications incorporate constant gear checking, proactive support, store network streamlining, quality control, upgrading proficiency, diminishing personal time, and further developing item quality.
-
Energy Sector
Have you considered power lattices that can distinguish and fix shortcomings all alone? This is made possible by the IIoT, which reduces downtime and ensures smoother operations.
-
Logistics and Transportation
From following shipments continuously to enhancing courses for conveyance trucks, IIoT is changing how products are moved worldwide.
Challenges Faced in IIoT Implementation
-
Security Concerns
As more devices connect, the threat surface expands. How do industries ensure their operations remain secure? Security worries in the Modern Web of Things (IIoT) relate to weaknesses that could prompt cyberattacks on basic foundations and modern systems. These concerns include data breaches, unauthorized access, device and network vulnerabilities, and the need for robust encryption and authentication measures to protect against potential threats and disruptions.
-
Integration Issues
Mixing old machinery with new technology poses challenges. How can industries integrate without halting operations?
The Future of IIoT
-
Emerging Trends
As 5G turns out to be far and wide, I anticipate that IIoT applications should be more productive and adaptable. Arising patterns in the Modern Web of Things (IIoT) incorporate edge registering for quicker information handling, simulated intelligence and AI for prescient examination, 5G availability for further developed correspondence, and expanded center around network safety to safeguard basic modern frameworks. These patterns drive IIoT’s advancement and effect across enterprises.
-
Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
With these technologies maturing, IoT devices will become more competent, learning from data and making even more informed decisions.
Conclusion Industrial IoT
The Industrial Internet of Effects is further than just a style. It’s an aIt instructional force driving diligence toward an effective, productive, and technologically advanced future. So, next time you hear about intelligent factories or connected machinery, remember – it’s part of the incredible world of Industrial IoT.
FAQs
Is IIoT safe?
While it has its challenges, advancements in security protocols are continually being made to ensure safe operations.
How is IIoT different from regular IoT?
IIoT focuses on industrial applications characterized by scale, security needs, and complexity.
What industries can benefit from IIoT?
Almost all – from manufacturing, energy, logistics, to even healthcare.
Is the adoption of IIoT expensive?
Initial costs might be high, but the long-term benefits of efficiency and savings outweigh the initial investment.
How much do you like our Article?
Rate our article (Industrial IoT: The Future of Smart Manufacturing)





